Posted by
Unknown
In:
Create your own retro analog effect

Once you have your photograph of choice, fire up Adobe Photoshop. This particular image I’ve sourced from ThinkStock.

Add a Curves adjustment layer to begin altering the tones of the image. Using an adjustment layer as opposed to the menu command gives you the ability to go back and tweak the settings, or remove them altogether.

Change the drop down menu to the Red channel and begin manipulating the curves. Tweak the line into an S shaped bend.

Move onto the Green channel, this time increase the green midtones by creating a large flowing bend in the line.

In the Blue channel, add both a slight S shaped bend and move the start and end points above and below the original curves line.

Fill a new layer with magenta, then change the blending mode to Soft Light. Reduce the opacity of the layer to around 20% to tone down the effect.

Press CMD+A to Select All, then go to Edit > Copy Merged (CMD+Shift+A). Paste this duplicate on a new layer, then add a Gaussian Blur. Add a Layer Mask to the blur layer and erase the blurring from the main subjects, leaving spots of blurring creeping in from the edges and in the background.

Dab spots of red using a large soft brush on a new layer. Change the blending mode of this layer to Linear Dodge to create a series of light leaks. Reduce the opacity to around 70%.

Select All, then right click the document and select Stroke. Add a 100px black stroke to the inside of the canvas.

Blur the stroke with maximum settings using the Filter > Blur > Gaussian Blur option to form a vignette. Set this layer to Soft Light at 70%.

Dab a large spot of white in the centre of the canvas to highlight the main subjects. Change this to Soft Light at 100%.

Fill a new layer with black and add some noise (Filter > Noise > Add Noise). Give the noise layer a slight Gaussian Blur to take the edge off the noise particles, then change the blending mode to Screen at 15%.

Posted on
-
0 Comments
Posted by
Unknown
In:
Create Vignette Effects with the Radial Filter in Photoshop CC

The original image.
And here’s what the final result will look like. Of course,
this is just one possible result using this specific image. What’s more
important, as with all of our tutorials, is that you’ll learn all the steps needed to create your own customized Radial Filter vignette effects with your own images: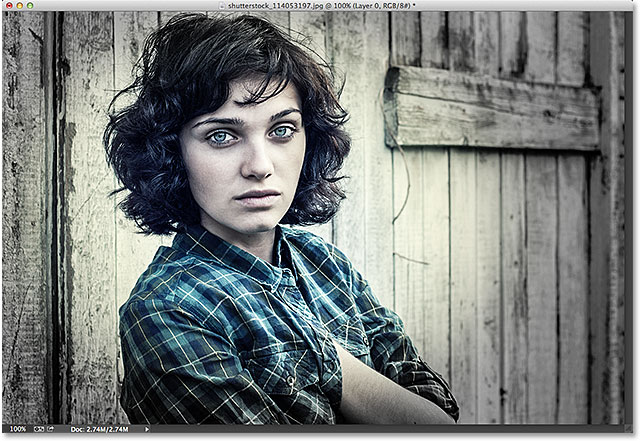
The final Radial Filter vignette effect.
Let’s get started!Step 1: Convert The Background Layer Into A Smart Object
We’ll start by converting the layer our photo is sitting on into a Smart Object. This way, the Camera Raw Filter will be applied as a Smart Filter, keeping the vignette effect itself fully editable while the original image remains untouched and unharmed. With my photo newly opened in Photoshop CC, if we look in the Layers panel, we see the image sitting on the Background layer:
The Layers panel.
To convert the layer into a Smart Object, click on the small menu icon in the top right corner of the Layers panel:
Clicking the Layers panel menu icon.
Choose Convert to Smart Object from the menu that appears: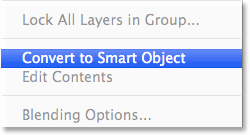
Choosing “Convert to Smart Object”.
Nothing will seem to have happened to the image in the document window, but a small Smart Object icon appears in the lower right corner of the layer’s preview thumbnail, letting us know that the layer is now a Smart Object:
The layer preview thumbnail displaying the Smart Object icon.
Step 2: Select The Camera Raw Filter
Go up to the Filter menu in the Menu Bar along the top of the screen and choose Camera Raw Filter: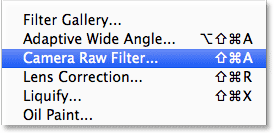
Going to Filter > Camera Raw Filter.
The image will appear inside the large Camera Raw dialog box. Technically, this is the Camera Raw Filter
dialog box, but with few exceptions, all of the tools, controls and
options that we’d find in the main Camera Raw dialog box are here: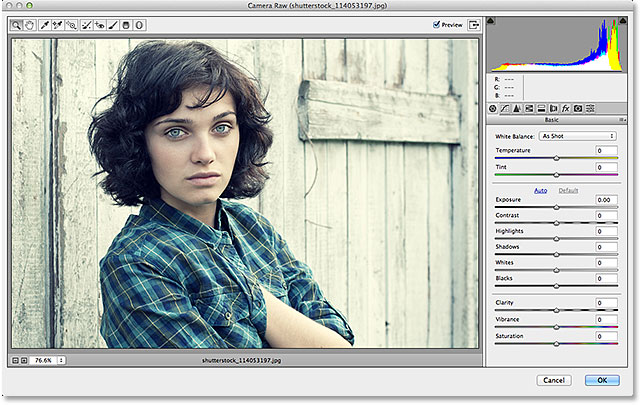
The Camera Raw (Filter) dialog box.
Step 3: Select The Radial Filter
Along the top left of the Camera Raw dialog box is where we find its various tools. Click on the Radial Filter to select it (it’s the last tool on the right):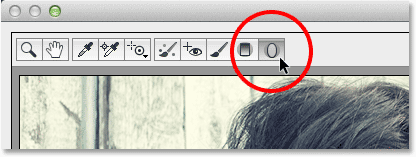
Choosing the Radial Filter.
Step 4: Lower The Exposure
With the Radial Filter selected, the panel on the right of the Camera Raw dialog box displays the Radial Filter’s various options for making adjustments to the image. Start by clicking the round minus icon ( - ) directly to the left of the word Exposure. This will set the Exposure slider to a preset value of -50, but the main reason we’re doing this is because it instantly resets all of the other sliders to 0, allowing us to focus just on the Exposure setting: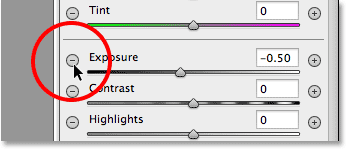
Clicking the minus icon to the left of the Exposure slider.
Then, click on the Exposure slider itself and drag it further to the left to a value of around -2.00.
This will give us a good initial darkening value to start with. The
image itself won’t appear any darker at the moment because we haven’t
yet added the actual filter, but we’ll do that next: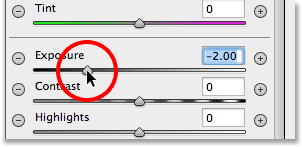
Setting the initial Exposure value to -2.00.
Step 5: Drag Out The Radial Filter In The Image
With the Exposure value lowered, click somewhere near the center of where you want your vignette effect to appear in the image. Then, with your mouse button still held down, drag outward from that point. You’ll see the elliptical Radial Filter shape appearing as an outline as you drag (if you want to force the Radial Filter shape into a perfect circle, press and hold the Shift key on your keyboard as you’re dragging). You can move the filter shape around inside the image as you’re dragging it by pressing and holding the Spacebar on your keyboard. Release the Spacebar once you’ve positioned the filter where you want it to continue dragging out its shape, then release your mouse button when you’re done: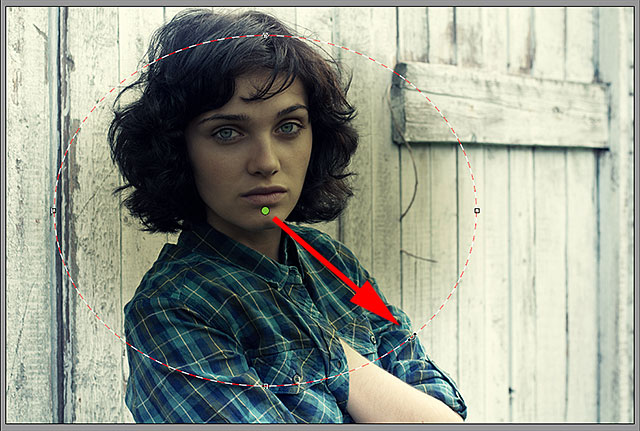
Dragging out the Radial Filter from its center.
The Outside / Inside Effect Option
Notice, though, that with my image, the inside of the Radial Filter shape is being darkened while the area outside the shape remains at its original brightness level. That’s the exact opposite of what I wanted for my vignette effect. If you’re seeing the same thing with your image, look down at the bottom of the Radial Filter options in the panel along the right (you may need to scroll down using the scroll bar along the right of the panel if you’re not in Camera Raw’s Fullscreen mode). There, at the bottom of the list, is an option called Effect with two checkboxes that control where the image adjustments are applied – inside the shape or outside. Mine is currently set to Inside so I’ll click the Outside option to change it: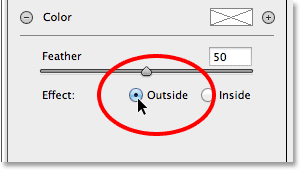
Changing the effect’s location from inside the shape to outside.
And now, we see the darkening effect appearing around the outside of the shape where it should be: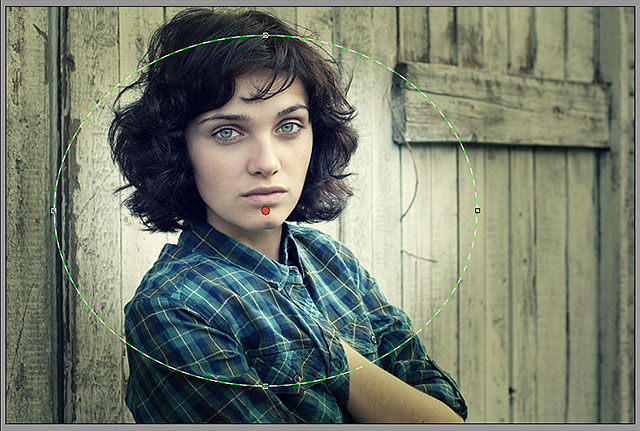
The effect after changing its location to Outside.
Resizing, Moving And Rotating The Shape
Once you’ve dragged out your initial Radial Filter shape, you can resize and reshape it, making it taller, shorter, wider or more narrow, by clicking and dragging any of the four handles (the little squares). You’ll find one at the top, bottom, left and right of the shape. You can continue moving the shape around inside the image if needed by moving your mouse cursor inside the shape. When your cursor changes to a four-pointed direction arrow, click and drag your mouse. Also, you can rotate it by moving your mouse cursor near the edge of the shape, then clicking and dragging when you see your cursor change into a curved, double-pointed arrow. In my case, I’m just going to make my shape larger by clicking and dragging the handles: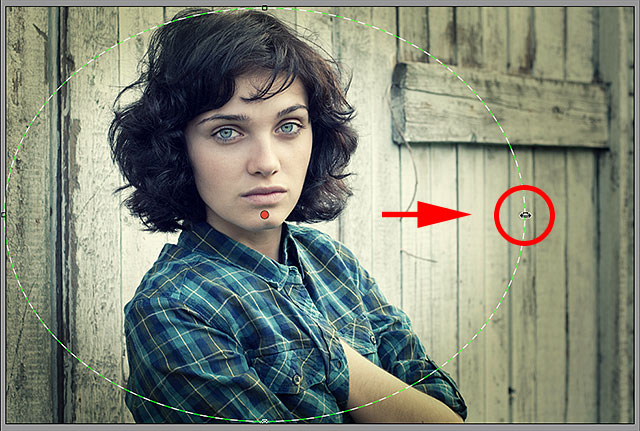
Dragging a handle to resize and reshape the filter.
Step 6: Adjust The Image Using The Sliders
Now that we’ve added the filter to the image, we can use the various image adjustment sliders in the panel along the right to make further changes to the effect. We can start by fine-tuning the Exposure amount to either darken the effect further or lighten it by clicking and dragging the slider left (darker) or right (lighter). But there’s a lot more we can do besides that. We have sliders for adjusting the contrast, the highlights and shadow areas, color saturation, and more! You can experiment with these sliders all you want because everything we’re doing to the image here is non-destructive, and you’ll see a live update of your changes to the image as you try different settings.For my image, I think I’ll darken the edges a bit more by lowering the Exposure value further to -2.20. I’ll bump up the contrast of the edges by increasing the Contrast value to +40. I’ll leave the Highlights and Shadow sliders alone for now, but I’ll drag the Clarity slider all the way to the right to increase it to its maximum value of +100 (Clarity increases or decreases contrast in the midtones of an image, and setting it to a high amount often creates a harsh, grungy look that I think suits my image well). Finally, I’ll drag the Saturation slider all the way to the left to -100 to remove all the color from the edges of the image. Of course, these are just the settings that I think work well with the specific image I’m using. The adjustments you make with your image may be different:
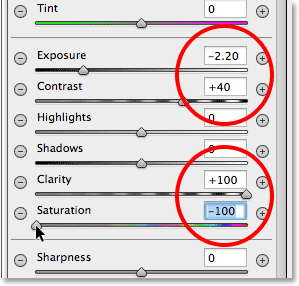
Changing the look of the image using the various adjustment sliders.
Adjusting The Feathering
We can also adjust the feathering amount for the vignette, or in other words, increase or decrease the size of the transition area between the main image in the center and the darker area surrounding it, by dragging the Feather slider left (to decrease it) or right (to increase it). You’ll find the Feather slider near the bottom of the options on the right (directly above the Outside / Inside Effect option):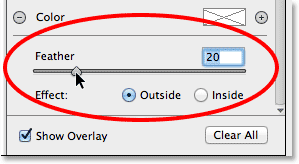
Adjusting the size of the transition area with the Feather slider.
Showing And Hiding The Overlay
To get a better view of what your vignette effect looks like, you can temporarily hide the Radial Filter overlay in the preview area by unchecking the Show Overlay option in the lower right of the Camera Raw dialog box. Select the option again to turn the overlay back on. Or, you can quickly turn the overlay on and off simply by pressing the letter V on your keyboard. Here, I’m unchecking the option to turn the overlay off: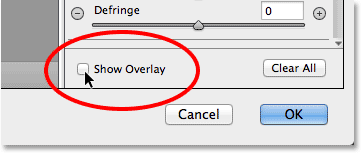
Unchecking the Show Overlay option.
And here’s what my image looks like so far with the overlay turned off: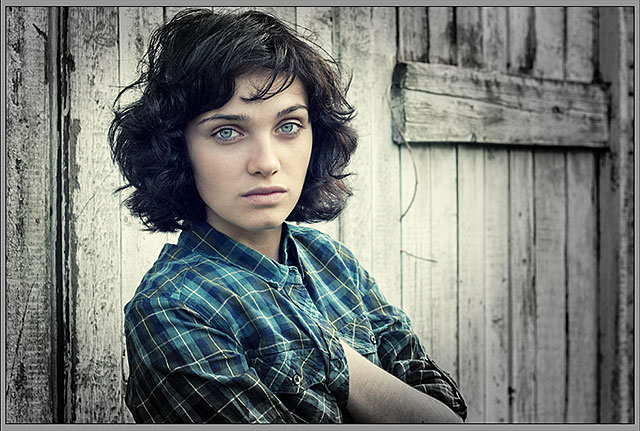
Turning the overlay off makes the effect easier to see.
Showing And Hiding The Preview
The reason we’re seeing a live preview of our changes to the image is because by default, the Preview option at the top of the Camera Raw dialog box is checked. We can turn the preview off at any time to compare our changes with the original image by simply unchecking the Preview option. Check it again to turn the preview back on. Or, you can press the letter P on your keyboard to quickly toggle the preview on and off:
The Preview option is located just above the top right corner of the preview area.
Step 7: Add A Second Radial Filter
One of the most powerful features of Camera Raw’s Radial Filter is that we can add additional Radial Filters to the same image, each with separate image adjustments! To add a new Radial Filter, select New at the top of the Radial Filter panel: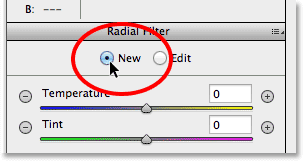
Selecting the New option.
Then, just use everything we’ve learned from adding our
initial filter to add the second one. First, click inside the image and
drag outward to create the new filter shape, holding down your Spacebar as you drag to reposition it if needed: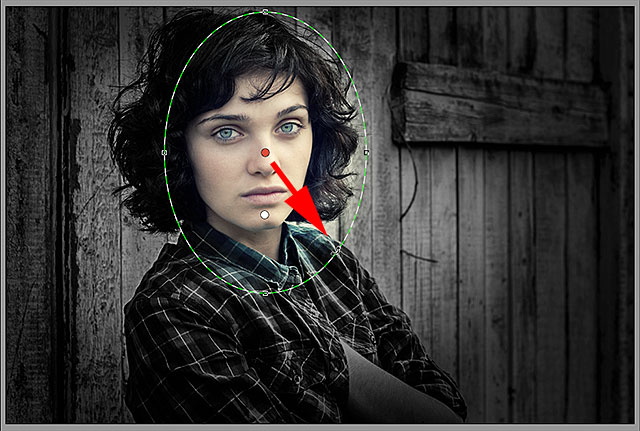
Clicking and dragging out a second Radial Filter.
Switching Between Radial Filters
Notice that there are now two round dots on my screen. Each dot represents one of the filters. At any time, we can switch between filters to re-adjust their settings simply by clicking on their dots. The currently active filter will have a colored dot while the other dot(s) appear white. Here, I’ve clicked on the initial filter’s dot to re-select it and make it active: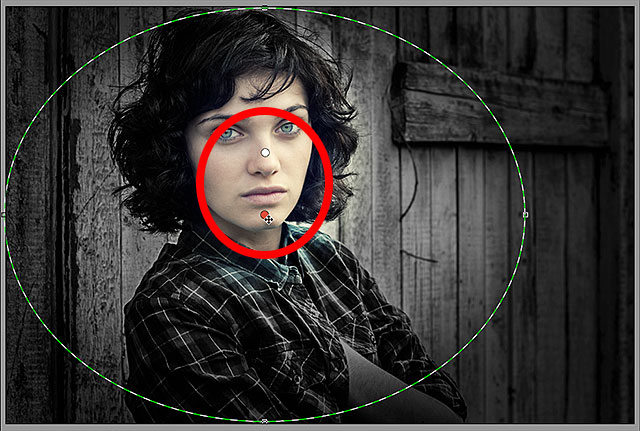
Switching back to the original filter by clicking its dot.
I’ll switch back to my new filter by clicking on its dot.
Notice that a couple of things are happening with this second filter.
First, all of my settings from the initial Radial Filter have been
copied to this second filter. We’ll change that in a moment, but the
second thing to notice is that my effect is again being applied outside
the shape. With this second filter, I want the effect to appear inside the shape, so once again, I’ll scroll down to the bottom of the Radial Filter panel along the right and switch the Effect option from Outside to Inside. Or, I could just press the letter X on my keyboard to instantly switch from Outside to Inside and vice versa: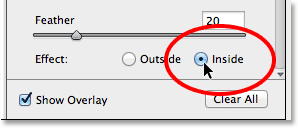
Changing the Effect option from Outside to Inside.
And now, the effect appears inside the second filter.
Notice also that the filter’s selection dot has changed from red to
green. A red dot means the effect is being applied outside the shape, while a green dot indicates it’s being applied inside: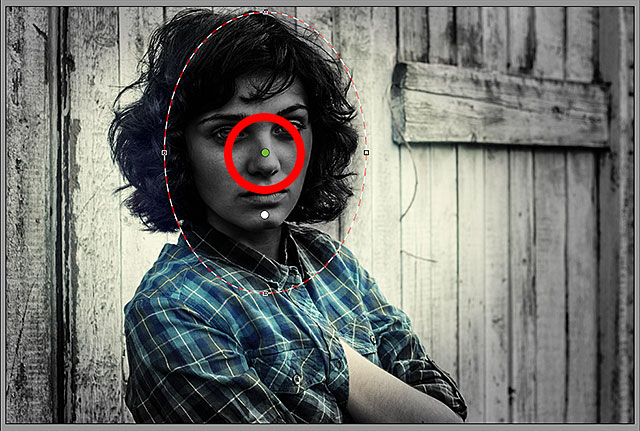
With the effect inside the shape, the filter’s selection dot has turned from red to green.
I’ll resize, move and rotate my second filter using the
steps we learned earlier, dragging the handles to resize and reshape it,
clicking and dragging inside the shape to move it, and clicking and
dragging near the edge of the shape to rotate it: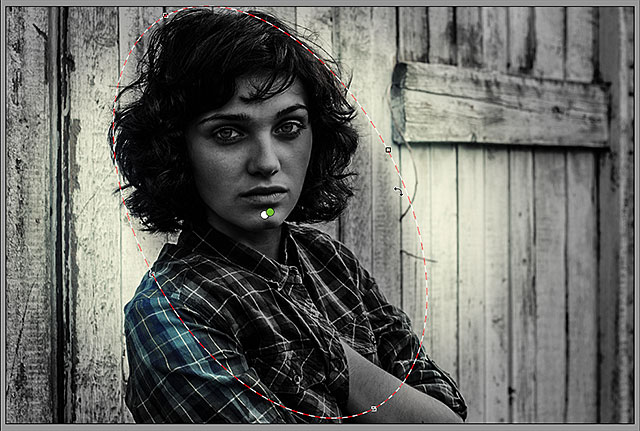
Using more of a narrow, diagonal shape for the second Radial Filter.
Next, I want to reset my image adjustment sliders in the Radial Filter panel, and another easy way to reset them is to double-click
on them. Here, I’ve double-clicked the Exposure, Contrast, Clarity and
Saturation sliders to reset them all to 0 (the others were already set
to 0):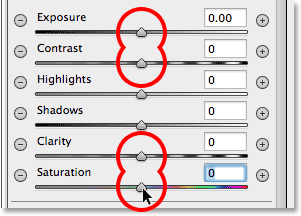
Double-clicking sliders to reset them.
Now that my second filter has been reset, this time I’ll
start by cooling down the overall color temperature inside the shape by
dragging the Temperature slider at the top of the panel a little to the left. A value of around -20 will add a slight blue color cast. I’ll leave the Tint slider directly below it set to 0 since I don’t want to add any green or magenta to the image. I’ll also leave the Exposure slider set to 0, but I’ll increase the Contrast to +50. Again, these are just settings that I’ve found, after some experimenting, that they work well with this particular image.I’ll dial down the highlights, bringing out a bit more detail in the lightest areas inside the shape, by lowering the Highlights value to around -25. Then I’ll do the opposite with the Shadows slider, increasing it to +25 to brighten up some of the darkest areas, again bringing out more detail. I’ll bump the Clarity value up to +50 to bring out more contrast in the midtones, and finally, I’ll lower the Saturation value to -30 to reduce the color saturation:
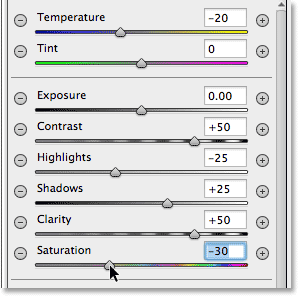
The image adjustment settings for the second Radial Filter.
Lastly, I’ll increase the size of the transition area for the second filter by bumping the Feather amount up to 50: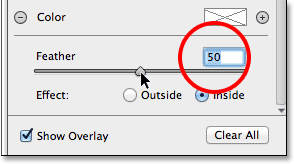
Increasing the Feather amount to 50.
Here’s what the image looks like now with both Radial Filters applied: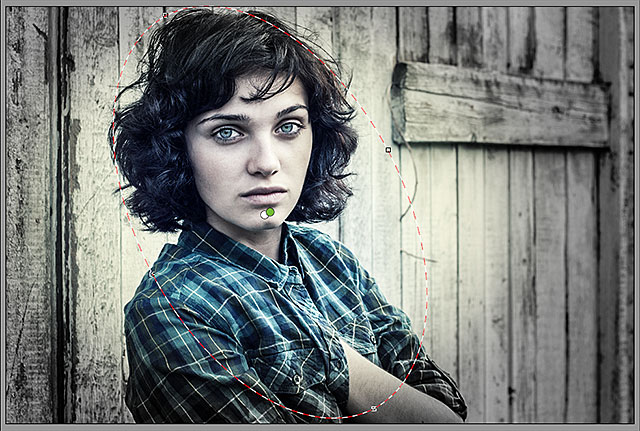
The image with the second Radial Filter’s adjustments applied.
Step 8: Close Out Of The Camera Raw Dialog Box
I’m happy with my effect, so I’ll click the OK button in the lower right corner of the dialog box to accept my settings and close out of the Camera Raw Filter:
Clicking the OK button.
If we look again in the Layers panel in Photoshop itself, we now see the Camera Raw Filter listed as a Smart Filter below the image. I’ll click on the Smart Filters visibility icon to temporarily hide the effects of the Camera Raw Filter from view in the document window:
Clicking the OK button.
This hides all of the changes I made with the Radial Filter
and re-displays the original image. Notice that it remains untouched
and unaffected by anything we’ve done:
The original image re-appears unharmed.
I’ll click again on the Smart Filter visibility icon to
turn the Camera Raw Filter back on, and now we see the final Radial
Filter vignette effect:
The final result.
And there we have it! That’s how to add a creative, fully
customizable and non-destructive vignette effect to an image using the
new Radial Filter inside the new Camera Raw Filter in Photoshop CC!
Posted on
-
0 Comments
Posted by
Unknown
In:
Membuat Foto Menjadi Kartun Dengan Photoshop
Dalam tutorial ini saya akan menjelaskan cara membuat foto anda menjadi gambar kartun dengan menggunakan photoshop. Tutorial ini memakai Adobe Photoshop CS2, tapi saya rasa langkah-langkah yang akan dijelaskan dalam tutorial ini bisa diaplikasikan pada photoshop versi-versi lainnya. Untuk membuat foto menjadi kartun dengan photoshop bisa dikerjakan dengan beragam teknik, salah satunya adalah teknik berikut ini:
Langkah 1: a. Buka foto yang akan anda edit di Adobe Photoshop. Dalam memilih foto yang akan anda jadikan kartun, sebaiknya pilih foto yang tajam (fokus) dan detil wajahnya terlihat dengan jelas. Foto yang buram, agak kabur, atau yang cenderung gelap, bukanlah pilihan yang bagus. Semakin besar resolusi foto maka akan semakin baik hasilnya. b. Duplikat layer tsb. Ubahlah nama layer baru tsb menjadi 'asli'. Layer 'asli' bisa anda pakai untuk 'menyimpan' foto aslinya, agar jika sewaktu-waktu dibutuhkan maka gambar aslinya masih ada. c. Kuncilah layer ini (klik tombol 'lock all' ), dan matikan visibility-nya. d. Buatlah layer baru. Ubah namanya menjadi 'background'. Anda akan memakai layer ini sebagai warna latar belakang untuk foto kartun anda. Isilah layer ini dengan warna oranye menggunakan tool Paint Bucket dan letakkan pada posisi paling bawah. Langkah 2: a. Pisahkan objek foto yang ingin dikartunkan dari background foto. Hapuslah bagian-bagian foto yang tidak diinginkan. Caranya, seleksi objek dengan menggunakan tool Pen. Dengan tool Pen, buatlah satu path di sekeliling objek, ubahlah path tsb menjadi selection (tombol: ctrl + Enter), inverse selection tsb (tombol: ctrl + shift + i), hapus (tombol: del), kemudian hilangkan garis selection (tombol: ctrl + D). Langkah 3: Langkah selanjutnya adalah membuat 'outline' objek foto anda. a. Duplikat layer 'Layer 0', kemudian ubah nama layer menjadi 'outline'. b. Lalu masuk menu: Image -> Adjustments -> Shadow/Highlight... Klik tombol OK. Langkah yang ini tidak harus Anda lakukan. Namun seringkali langkah ini akan membuat hasil outline anda nantinya menjadi lebih tajam. c. Pastikan warna di color palette adalah hitam untuk foreground dan putih untuk background. (Ketik 'd' pada keyboard jika warna di color pallete bukan warna default tsb). d. Ubah gambar menjadi outline dengan menggunakan filter Photocopy. klik menu: Filter -> Sketch -> Photocopy... Set 'Detail' ke 3. Set 'Darkness' ke 8. Klik tombol 'OK' Hasil yang diinginkan adalah outline gambar terlihat detil namun tidak sampai menyebabkan outline terlihat 'kotor' penuh bercak hitam. e. Ubah garis-garis outline menjadi garis hitam solid. Klik menu: Image -> Adjustments -> Threshold... Geserlah slider ke kanan dan kiri, sambil dilihat previewnya, sampai preview yang tampil terlihat paling bagus (outline terlihat detil akan tetapi tidak kotor penuh bercak). Klik tombol OK. Langkah 4: Langkah selanjutnya adalah mewarnai badan. a. Pilih / aktifkan layer 'outline'. Kemudian tekan Ctrl-J untuk menduplikasi layer . Ubahlah nama layer menjadi 'white'. b. Selanjutnya kita ubah warna layer ini menjadi putih.Geser slider 'Brightness' hingga mentok kanan (+100) dan slider 'Contrast' hingga mentok kiri (-100). Klik OK. Anda akan mendapatkan hasil seperti ini: c. Pindahkan posisi layer 'white' ke bawah layer 'outline'. d. Ubah blending mode layer 'outline' menjadi 'Multiply'. e. Tekan tombol 'd' untuk mengembalikan warna foreground dan background ke default (hitam untuk foreground, dan putih untuk background) f. Pilih / aktifkan layer 'white' pada Layers Palette. g. Klik 'Create new fill or adjustment layer' pada bagian bawah Layers Palette. Pada menu popup yang muncul, pilih 'Solid Color...'. Selanjutnya akan muncul kotak dialog 'Color Picker'. Pada 'Color Picker', pilihlah warna coklat krem (#FAD594). Warna ini akan anda jadikan sebagai warna kulit. Klik OK h. Hasilnya seperti ini. i. Pilih tool 'Paint Bucket Tool' . Klik pada kanvas untuk mengisi layer mask dengan warna hitam. j. Ubahlah nama layer menjadi 'skin'. Hasilnya akan seperti ini. k. Buatlah clipping mask antara layer 'skin' dengan layer 'white'. Tekan Ctrl + alt + G dalam keadaan layer 'skin' sedang aktif / terpilih. l. Pada 'Layers Palette', klik layer 'outline' sambil menekan tombol Ctrl. Cara ini akan menyeleksi foto anda. m. Tekan tombol 'x' untuk menukar warna foreground dengan warna background. n. Pilih tool 'Paint Bucket' , klik pada bagian dalam seleksi di kanvas untuk mengisinya dengan warna putih o. Tekan Ctrl + D untuk membatalkan seleksi. Langkah 5: Memberikan Shading Suatu gambar yang 'datar' tidak akan terlihat menarik. Anda bisa memberikan shading pada gambar anda supaya memberikan kesan kedalaman (3 dimensi), caranya: a. Duplikat layer 'Layer 0', beri nama 'Layer 0 copy', lalu pindahkan layer ini ke atas layer 'outline'. b. Kaburkan (blur) sedikit layer ini. Pilih menu: Filter -> Blur -> Gaussian Blur... Set radius efek blurring ke 4 pixels. Klik Ok c. Pilih menu: Filter -> Artistic -> Cotout... Set 'Edge Simplicity' ke 2. Set 'Edge Fidelity' ke 1. Klik OK pada kotak dialog Cutout d. Ubahlah nama layer 'Layer 0 copy' menjadi 'shade'. e. Pilih menu: Image -> Adjustments -> Threshold... Klik tombol OK jika Anda sudah puas dengan hasilnya. f. Pilih tool 'Magic Wand Tool' pada 'Tools Palette'. g. Klik pada area berwarna putih pada kanvas. h. Tekan tombol Delete (pada keyboard) untuk menghapus bagian berwarna putih pada layer 'shade'. i. Tekan tombol Ctrl + D untuk menghilangkan seleksi. j. Ubahlah blending mode layer 'shade' menjadi 'Soft Light'. Ubah opacity menjadi 40%. Nah, kita sudah selesai dengan shade-nya. Mari kita lanjutkan dengan tint-nya. Langkah-langkah pembuatan tint pada prinsipnya sama dengan cara pembuatan shade. k. Pilih / aktifkan layer 'tint'. l. Pilih menu: Image -> Adjustments -> Threshold... Geserlah slider ke kiri dan kanan. Bereksperimenlah dengan slider ini sambil terus memperhatikan preview hasilnya. Klik tombol OK jika Anda sudah puas dengan hasilnya. m. Pilih tool 'Magic Wand Tool' pada 'Tools Palette'. n. Klik pada area berwarna hitam pada kanvas. o. Tekan tombol Delete (pada keyboard) untuk menghapus bagian berwarna hitam pada layer 'tint'. p. Tekan tombol Ctrl + D untuk menghilangkan seleksi. q. Ubahlah blending mode layer 'tint' menjadi 'Soft Light'. Ubah opacity menjadi 60% (bereksperimenlah dengan nilai opacity ini sampai Anda mendapatkan hasil yang pas). Langkah 6: Langkah selanjutnya adalah pewarnaan. a. Pilihlah tool 'Paint Bucket Tool' pada Tools Palette (atau tekan tombol 'G'). b. Tekan tombol 'd' untuk mengembalikan warna foreground dan background ke warna defaultnya (hitam untuk foreground dan putih untuk background). c. Pada Layers Palette, pilih / aktifkan layer 'skin'. d. Klik 'Create new fill or adjustment layer' pada bagian bawah Layers Palette. Pada menu popup yang muncul, pilih 'Solid Color...'. Selanjutnya akan muncul kotak dialog 'Color Picker'. e. Pada kotak dialog 'Color Picker', pilihlah warna biru. Warna ini akan anda pakai sebagai warna baju. Klik tombol OK f. Klik kanvas untuk mengisi layer mask baju dengan warna hitam. g. Ubahlah nama layer menjadi 'baju1'. h. Buatlah clipping mask antara layer 'baju1' dengan layer 'skin'. Tekan Ctrl + alt + G di saat layer 'baju1' sedang aktif (terpilih). i. Lakukan lagi langkah-langkah di atas untuk membuat layer-layer untuk warna bibir, mata, iris, dan rambut dll. j. Setelah layer-layer untuk warna siap, anda dapat mulai mewarnai tiap bagian dari gambar anda. Mulai dengan mewarnai rambut. Pilih 'Pencil Tool' pada 'Tools Palette' (atau tekan tombol 'B' pada keyboard). k. Aktifkan / pilih layer 'rambut(color fill)' pada 'Layers Palette'. l. Pastikan bahwa warna foreground adalah putih. (Tekan tombol 'X' jika Anda butuh untuk menukar warna foreground dengan warna background). m. Mulailah mewarnai rambut. Gunakan hard brush dengan opacity diset pada angka 100%. Saat mewarnai pastikan bagian rambut Anda zoom-in agar pewarnaannya rapi tidak keluar dari batas gambar rambut. (Clipping mask yang telah kita buat pada langkah sebelumnya sangat membantu dalam hal ini. Warna yang anda sapukan tidak akan keluar dari objek gambar dan mengotori background) n. Selanjutnya ulangi step l hingga m untuk mewarnai iris. Hasilnya seperti ini:
Posted on
-
1 Comments
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

































